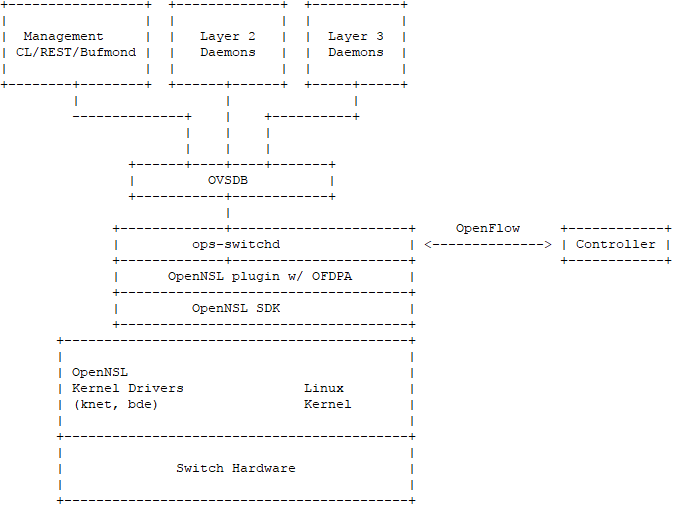
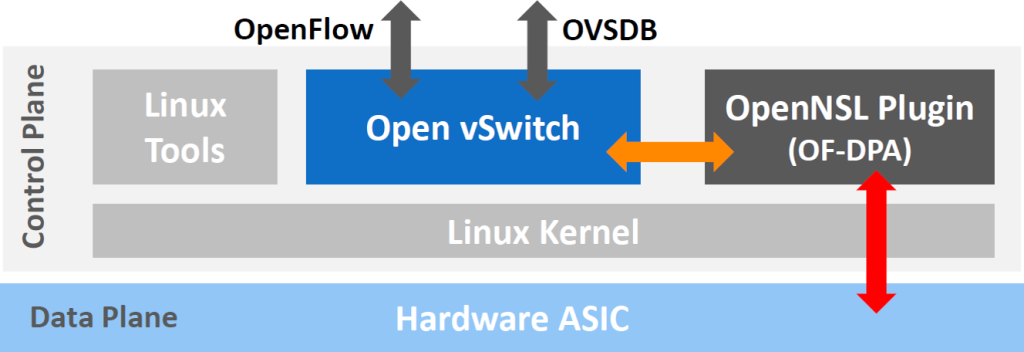
At first, OpenSwitch project and openswitch.net were governed by HP as they tried to ride the “open networking” wave. An open community, a lot of talk-based supports from several vendors, all as usual.
Efforts were made to create a set of protocols and an SAI connector to make adoption of new silicon easier.
After about 8 months, the project was handed to the Linux Foundation. A proper excuse was made – HPE said the move was a way to show the community that this wouldn’t be an effort controlled by one vendor.
We think that they simply realized that they are not making enough money out of this.
Four more months later, the project was overtaken by Dell. What a joke after an excuse from HPE about one vendor control.
This was the moment of OPX birth. All previous efforts were set to zero, and a totally new system was born. Dominated by Dell, running only on Dell, and claiming the same set of goals – openness, disaggregation, modularity, etc.
What About OPS?
and anyone can work with it.
That’s how Netberg made OpenSwitch 2.0 – by taking the OPS code and implementing new features and fixing bugs.